About HTML
All web documents are created in HTML. HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup or formatting language. It defines the way a document should look when printed or displayed.
Some Information You May Need to Know About HTML
You do not need to know HTML but you will need to keep a few simple rules in mind when laying out documents.
HTML is NOT Word and Word is NOT HTML
- A Word document is a document in a file format created for the Microsoft Word program.
- All web documents are created in HTML.
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup or formatting language.
- It defines the way a document should look when printed or displayed.
- It also enables the linking of documents so the reader can click to navigate from one document to another.
- These links are what make the internet so useful.
- You do not need to know HTML, but you will need to keep a few simple rules in mind when laying out documents.
Be aware! When you copy and paste your text directly from a word document into the HTML text editor, it copies the word syntax along with the text. Hence, it contains hidden syntax that can make your text size and font seem different to the other text on the page.
Converting a document to HTML requires the removal of the MS Word syntax.
If you need to copy and paste from a word document, copy your text and use the paste from word option on the toolbar. Find more information onImporting text into WebEd
Hyperlinks
- The linking of documents so the reader can click to navigate from one document to another.
- These links are what make the Internet pages so useful and allow easy jumping from one place to another
Styles
- Styles are universally applied to your website and controlled through one document, your Style Sheet.
- Speak to your consultant about including extra styles in your style sheet.
- When editing, select from the palette of existing styles to keep the formatting consistent
Tables
- Tables are an easy way to layout pages in HTML
- Some designs have moved away from tables and now use content snippets to achieve the same results
- This can make some content more difficult to edit, speak to your consultant about your site
- Tables do not necessarily have to have visible borders.
A Quick Word About Design
Planning a website is important, so take the time to plan exactly what is needed in your website. Thoroughly considering the audience or target market, as well as defining the purpose and deciding what content will be developed are extremely important. Do your Marketing Plan first. Decide exactly why you want a website, what you want the site to do for your business and what steps you will take to make that happen.
When planning a website consideration needs to be made of the following basic aspects of design:
- The content: the substance, and information on the site should be relevant to the site and should target the area of the public that the website is concerned with.
- The usability: the site should be user-friendly, with the interface and navigation simple and reliable.
- The appearance: the graphics and text should include a single style that flows throughout, to show consistency. The style should be professional, appealing and relevant.
- The visibility: the site must also be easy to find via most, if not all, major search engines and advertisement media.
With careful forethought of these points and with WebEd you can develop an effective website simply and quickly.
About The Editor
-
1The WebEd editor allows you to quickly create and update content and consists of a series of icons much like you would expect to see in any 'Microsoft' application.
-
2Below is an image of the toolbar you will see when you create a new page or edit an existing page.

-
3To determine the toolbar options, just mouse over each icon.
-
4An icon description or name with a pop-up explaining its use.
In the image below the Preview, the icon has been pointed to with the mouse revealing the "Preview content in-page" tooltip.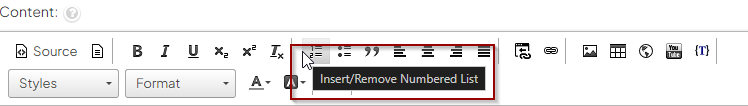
Clearing Cache
What is a cache?
A cache, pronounced CASH is hardware or software that is used to store something, usually data, temporarily in a computing environment. It is a small amount of faster, more expensive memory used to improve the performance of recently or frequently accessed data. Cached data is stored temporarily in an accessible storage media local to the cache client and separate from the main storage. The cache is commonly used by the central processing unit (CPU), applications, web browsers, and operating systems. The cache is used because bulk or main storage can't keep up with the demands of clients. Cache decreases data access times, reduces latency, and improves input/output (I/O). Because almost all application workloads depend on I/O operations, the caching process improves application performance.
What does clearing a cache do?
Memory on a device is made available by clearing the cache. Files downloaded straight from the web are kept in memory by a browser cache. Clearing it can solve user issues, such as the following:
- Applications with full cache memory risk crashing or loading incorrectly.
- Old caches can contain outdated information and files, causing webpages to not load or load incorrectly. Clearing them can get rid of outdated information.
- Personal data kept in browser caches, such as passwords, is also there. The user can be protected by clearing them.
- Most browser caches can be cleared by going to settings.
A cache should be cleared periodically, but not daily. Clearing the cache too often is not a good use of resources because of these issues:
- The user loses the benefit of quick file access;
- Caches delete some files on their own and don't need this sort of maintenance; and
- The computer will cache new files and fill the space up again.
Why Clear Cache?
Clearing the cache and cookies from a web browser is an important first step for almost any troubleshooting for internet browsing. The 'cache' is a tool used by your internet browser to speed up the page-loading process. However, sometimes it can cause a problem when websites are updated and developed as files saved in the cache may conflict with what's actually coded into the website. Clearing cache and cookies is a way to ensure that any issues you may come across are actually something wrong with the website, rather than inconsistencies caused by using different browsers.
Clear Your History (Cache) in Any Browser
Chrome
-
1Click the Tools menu (three dotted lines in the upper-right corner).
-
2Select History.
-
3Select Clear Browsing Data from the left-hand side. Set the Time Range set to All Time. Check-mark Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files and select Clear Data.
-
4If on a Windows computer, close and re-open Chrome to save your changes. If on an Apple computer, go to the Chrome menu on the top menu bar and select Quit for the changes to take effect.
Firefox
-
1Click on the Tools bar (three bars in the top-right corner).
-
2Click History.
-
3On the menu to the right, select Clear Recent History.
-
4In the Clear All History menu, select the time range to Everything.
-
5Select the options, Cookies, Cache, Active Logins, Site settings, and Offline website data.
-
6Click OK.
-
7If on a Windows computer, close and re-open Firefox to save your changes. If on an Apple computer, go to the Firefox menu on the top menu bar and select Quit for the changes to take effect.
Solution on Mobile Menu not Showing
How to fix the Menu not Showing issue
- Bootstrap menu element has data, role and aria attributes that need to be on the element
- These are the lines of codes which are not implemented on the existing site templates like SSEO, IP and WSP before it was fixed.
- The following code was added: data-toggle="dropdown" role="button" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false"
Guide to Fix The Menu Not Showing Issue
-
1Log in as an administrator and go to the Admin Dashboard.
Learn how to log in here → -
2Go to System Settings > Module Management > Curly Bracket Tags
-
3Look for Menus under the column Name and click Edit
-
4On the line code #if (node.Children.Any()) from the children menus add the data-toggle="dropdown" role="button" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false" inside the < a > code shown on the image below
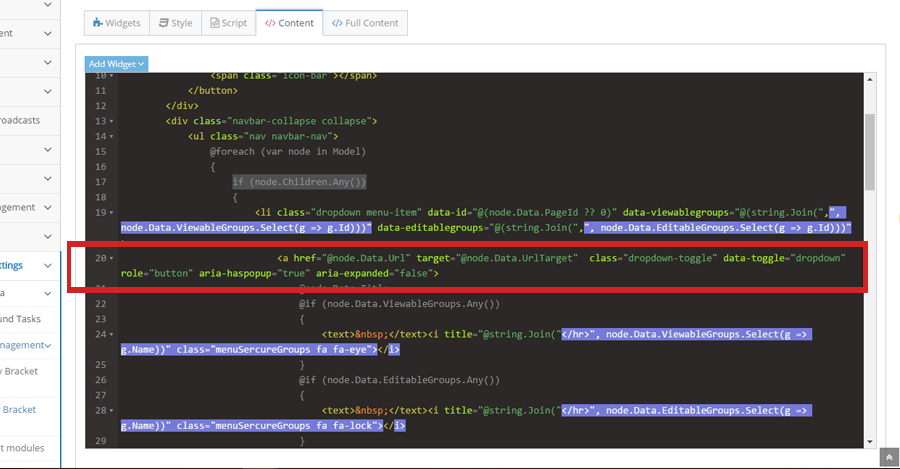
-
5Test the mobile menu
Remove YouTube Ads
Note that You must be logged in at YouTube and have administrator privileges to update the account settings.
-
1Log in to your YouTube account
-
2Click on the settings menu
-
3Click on the radio button that says 'Do not allow advertisements...'
-
4Click on the Save button on the upper right corner of the page
YouTube: Stop Related Videos
This guide assumes that you are embedding the video into a webpage (not the video film strip) and have already the YouTube embed code.
Using YouTube Embed Code
-
1Add the '?rel=0' parameter at the end of the YouTube URL. This will allow the YouTube player to show suggested videos related to your YouTube video.
Example:
- Copy the code and paste it on the Embed YouTube Video window as shown below:
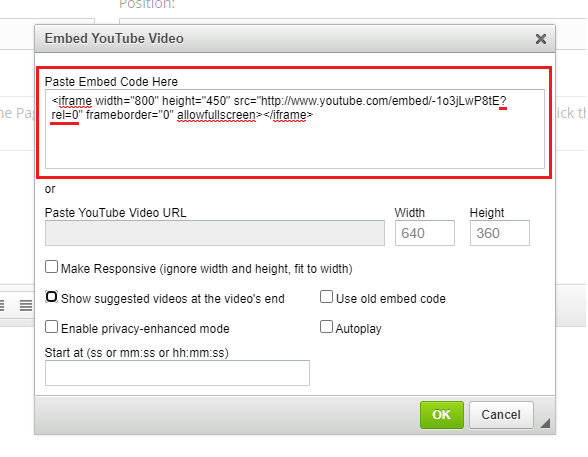
-
2To make the video responsive using the embed code, add the following attributes on the iframe tag:
Example: style="position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0;width: 100%;height: 100%;"
-
3Click OK
-
4YouTube video is now pasted on the editor
Using YouTube URL
-
1Copy and paste the YouTube URL on the Embed YouTube Video window as shown below:
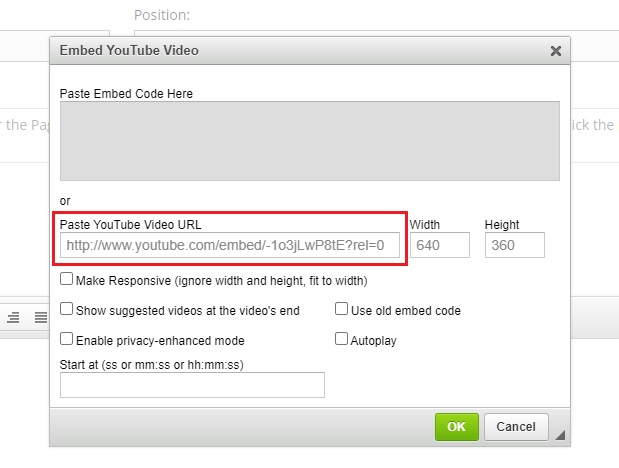
-
2You may remove the ?rel=0if you wish to show suggested videos not related to your YouTube video.
-
3To make the video responsive, tick the checkbox for Make Responsive.

-
4To show suggested videos at the end of the video, tick the checkbox corresponding to Show suggested videos at the video's end.
-
5Untick if you wish not to show suggested videos.

-
6Click OK
Note: Your YouTube video is now successfully added to the editor of the page you are creating.